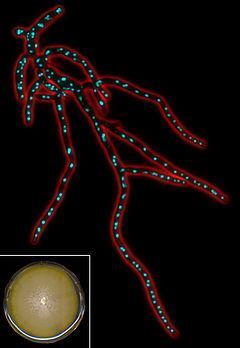
Fluorescent micrograph of Ashbya gossypii mycelium. Image source:
wikipedia
The genome sequence and gene predictions of Ashbya
gossypii were not determined by the JGI, but were downloaded
from NCBI
and have been published (Dietrich FS
at al., 2004).
The filamentous fungus
Eremothecium gossypii, also known
as Ashbya gossypii, was first described in 1929 as a
cotton pathogen transmitted by sucking insects. In addition to
cotton, it infects other agricultural crops such as citrus fruits.
It is likely better known as an appealing model to study
filamentous growth due to the following characteristics, being
haploid with a small genome, efficient gene targeting, propagation
of plasmids and growth on defined media. E. gossypii is
used in industry for the production of riboflavin.
Genome Reference(s)
Please cite the following publication(s) if you use the data from this genome in your research:
Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pöhlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P
The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome.
Science. 2004 Apr 9;304(5668):304-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1095781
Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pöhlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P
The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome.
Science. 2004 Apr 9;304(5668):304-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1095781
Reference
- Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pöhlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P. The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Science. 2004 Apr 9;304(5668):304-7. Epub 2004 Mar 4. PubMed PMID: 15001715.
