|
Functional annotations can be generated automatically or assigned independently by the user. The Functional (Protein) Annotation area includes a User-Assigned Ontology area for entering new user annotations, an Automatic Ontology area that allows users to easily create a user annotation based on an automatic one, and a High-Scoring Alignments area that allows users to easily create a user annotation based on GO or EC information assigned to an alignment hit.
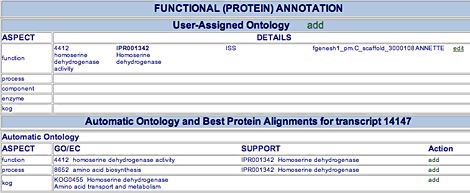
User-Assigned Ontology Annotations
Annotators can assign GO terms, EC numbers in the User-Assigned Ontology area.
To add an annotation, click the add button beside the "User-Assigned Ontology" heading. In the new window, enter a GO ID or EC number in the GO/EC ID field. In the Support field, enter a description of the evidence for making this assignment. Select an evidence type from the Code menu, and enter any notes in the Note field. Click Save Item to save your changes. The annotation will appear in the User-Assigned Ontology table opposite the ontological aspect it represents (function = molecular function, process = biological process, component = cellular component, enzyme = EC information, and KOG = KOG information). You may have to reload the web page to see your new annotation.
To add to an existing user-assigned functional annotation, click the edit button beside it. In the new window that opens, you will see the existing annotation. Enter a note in the Note field, then click Save Item.
To remove an existing user-assigned functional annotation, click the edit button beside it. In the new window that opens, click Delete Item.
Automatically Assigned Ontology Annotations
Automatically assigned ontology terms are shown in the Automatic Ontology area. Information for each annotation includes
- Aspect The molecular function ("function"), biological process ("process"), cellular component ("component"), EC number ("enzyme"), or KOG ID ("kog").
- GO/EC The Go ID or EC number and description
- Support Evidence for the automatic annotation
- Action The add button, used to add a new user annotation based on the automatic one
An annotator can add a user annotation based on an automatic annotation.
To create a user annotation based on an automatic functional annotation, click the add button beside the automatic annotation. In the small window that opens, you can enter a note in the Comment field, then click Save Item. The annotation will then appear in the User-Assigned Ontology table. You may need to reload the web page to see the new user annotation.
High-Scoring Alignments
The High-Scoring Alignments area offers a quick way to add a functional annotation based on a Smith-Waterman alignment, provided the hit has GO or EC information associated with it. This area shows the highest scoring alignments for the gene model you are annotating. For each hit, you will see the defline and an image of the alignment, showing the positions in the hit sequence of the first and last amino acid of the alignment. Open areas within the dark blue rectangles denote gaps of more than three amino acids in the translated gene sequence that do not have corresponding sequence in the matched protein. Red areas indicate extra sequences of more than three amino acids in the matched protein that do not have a corresponding sequence in the translated gene. The width of the red area below the blue line indicates the length of the extra sequence.
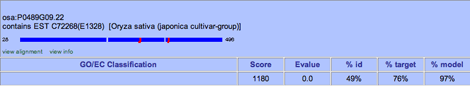
Just below the alignment image are two buttons.
Click view alignment to see the protein alignment report for the hit against the translated gene.
Click view info to go to the external database's record for the hit.
Information about the hit includes
GO/EC Classification The list of GO IDs (MF = molecular function, BP = biological process, and CC = cellular component) or EC numbers (EC) assigned to the hit. Each of these has an add button, which will allow you to add a user annotation based on the hit.
Score The alignment score for the protein against the translated gene
Evalue The E-value for the alignment (the number of times a match against the database is expected to occur by chance alone).
%id The percentage of the alignment length that contains identical amino acids in both the translated gene and the protein.
%target The percentage of the hit's length that is similar to the model.
%model The percentage of the model's length that is similar to the hit.
If a hit has a GO or EC assignment, you can use the alignment listing to quickly enter an annotation based on it.
To add a functional annotation supported by a particular alignment hit, click the add button next to the GO term or EC number for the hit (in the GO/EC Classification column). A new window will open with the GO or EC information and a description of the hit as supporting data already filled in. Enter any notes in the Comment field and click Save Item. You may need to reload the web page to see the new user annotation.
|