The JGI Genome Portal presents JGI-sequenced genomes through a variety of bioinformatics tools for search, visualization, and analysis. This page serves as jumping off point for Help, linking you to
Quick Tips
Be sure toRegister and log in!
Use the Genome/Tool Selector to navigate to theOrganism Portaland tool of your choice.
The primary elements of the JGI Genome Portal are listed below:
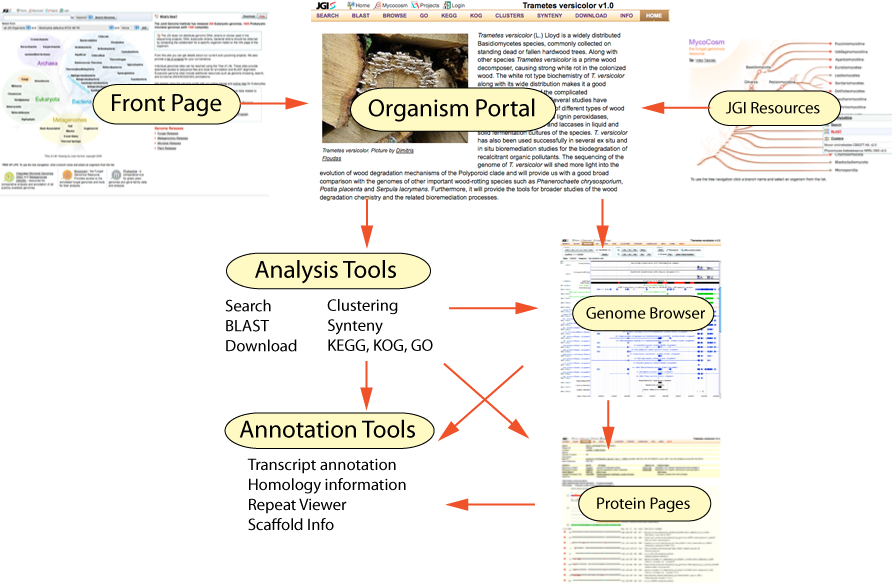
1.The Portal Front Page. The Front page is the navigational hub of the portal, from which you select the organism portal and tools you would like to work with.
2.Organism Portals: Each genome sequenced at the JGI can be accessed through its organism portal. The organism portal provides access to sequence data as well as to the set of tools available for use with this organism, such as search, BLAST alignment, functional annotation (GO, KEGG, KOG), and the Genome Browser. In Portal 6.0, we have also introduced organism "Group" portals, which provide search, BLAST, and download tools for groups of related genomes.
3.The Genome Browser: The Genome Browser is the primary visualization and navigation tool for exploring genome data and annotations.
4.Protein pages: Each gene model described within JGI genomes is associated with a web page that serves as the locus of information for this model, including it's sequence, functional annotation, predicted domains, and known homologs. Analogous pages also exist for ESTs, repeats, and alignments.
5. Integration with other JGI resources: The portal is connected in a variety of ways to other JGI resources such as the JGI Program Sites, IMG, VISTA, Phytozome, MycoCosm, and PhycoCosm. For instance (as is shown in the diagram below) fungal organism portals can be reached directly from the MycoCosm fungal program site.

These resources are interconnected in many ways, illustrated in the above figure, showing the navigational flows among tools in the Genome Portal. For instance, a Protein page for a particular gene model can be reached (among many other ways):
Similarly, the Genome Browser can be reached by selecting this tool in the organism portal header tab, by clicking on "Location" within a protein page, or by clicking on "G" for a hit within Advanced Search.
For each Organism Portal, a list of tools available for this Genome is listed in a tab bar across the top of the organism page. These tools are described below. Not all tools are available for all organisms. For instance eukaryotic genomes generally have a different set of tools available for use than do prokaryotic organism portals.
The "simple"Search tool allows you to search forInterPro domain predictions or Smith-Waterman alignments to one or more JGI-predicted genes (gene models). You can also jump to a specific JGI gene model.
TheAdvanced Search/Annotation tool provides powerful search features such as wildcard searches, searches against homologous proteins, and iterative searches. The tool also provides links to the Genome Browser and Protein page views of results and to the locus and transcript annotation areas.
TheBLAST tool provides an interface to NCBI'sBasic Local Alignment Search Tool, BLAT and other alignment search programs for queries against JGI genomes.
JGI'sGenome Browser lets you browse through JGI-predicted genes, view sequences, and study detailed alignments with nucleotide and amino acid sequences from relevant sequence databases.
TheGene Ontology tool uses theGene Ontology Consortium's controlled vocabulary for organisms to present information about JGI-predicted genes that have automatically assigned GO terms.
TheKEGG tool uses theKyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes and its hierarchies of metabolic and regulatory pathways to present information about JGI-predicted genes that have automatically assigned KEGG terms.
TheKOG tool uses euKaryotic Orthologous Groups from NCBI, a classification system based on orthologous relationships between genes in eukaryotes, to present information about JGI-predicted genes that have automatically assigned KOG identification numbers.
The Clustering tool allows you to investigate gene-family clusters. Clusters are pre-computed using anMCL-based algorithm performed on a set of protein sequences generated from BLAST and filtered using a spare dynamic programming approach.
The VISTA synteny application provides you with three different visualization tools for examining whole-genome DNA alignments.
TheDownload feature allows you to download any available data related to a given organism including assembled genomes, gene models, predicted protein files, ESTs, and transcripts.