This species was sequenced as a part of the Aspergillus whole-genus sequencing project - a project dedicated to performing whole-genome sequencing of all members of the Aspergillus genus. The Aspergilli is a ubiquitous and species-rich genus, currently containing more than 300 filamentous fungi. The genus covers a wide range of phenotypes and has a substantial economic foot print, as it includes fermenters of foodstuffs, key cell factories for production of enzymes and organic acids, plant pathogens, model organisms for cell biology, human opportunistic pathogens, producers of animal and human mycotoxins, and degraders of a wide range of organic biomass relevant for bioenergy conversion.
Aspergillus piperis (MB 500009)
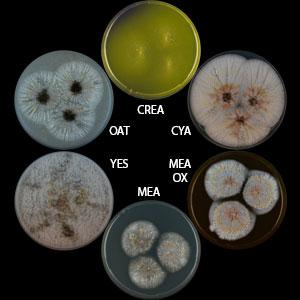
A. piperis Frisvad & Samson was described in Stud Mycol 50: 23-43, 2004 (on page 39). This species is placed in the A. niger clade (Varga et al., Stud Mycol 69: 1-17, 2011). It has been found on pepper of tropical origin, imported to Denmark. Sclerotia are produced on all media at the expense of conidial structures. Sclerotium borne exometabolites include 10,23-dihydro-24,25-dehydroaflavinine, and aurasperone B has also been reported from this species. This species is potential candidate for bioindustrial applications.
Genome Reference(s)
Vesth TC, Nybo JL, Theobald S, Frisvad JC, Larsen TO, Nielsen KF, Hoof JB, Brandl J, Salamov A, Riley R, Gladden JM, Phatale P, Nielsen MT, Lyhne EK, Kogle ME, Strasser K, McDonnell E, Barry K, Clum A, Chen C, LaButti K, Haridas S, Nolan M, Sandor L, Kuo A, Lipzen A, Hainaut M, Drula E, Tsang A, Magnuson JK, Henrissat B, Wiebenga A, Simmons BA, Mäkelä MR, de Vries RP, Grigoriev IV, Mortensen UH, Baker SE, Andersen MR
Investigation of inter- and intraspecies variation through genome sequencing of Aspergillus section Nigri.
Nat Genet. 2018 Dec;50(12):1688-1695. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0246-1
