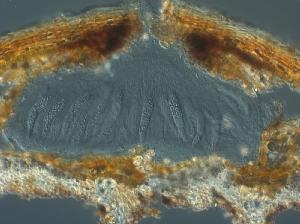
Image Credit: Pedro Crous
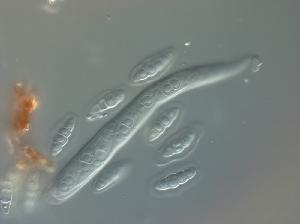
Image Credit: Pedro Crous
Massarina is a genus of fungi in the family Massarinaceae (Dothideomycetes). Dothideomycetes is the largest and most diverse class of ascomycete fungi. It comprises 11 orders 90 families, 1300 genera and over 19,000 known species.
Massarina was proposed by Saccardo (1883) for species
of pyrenocarpous ascomycetes with hyaline ascospores that had
previously been placed in Massaria De Not. In Massarina,
the ascospores are 2-celled or multi septate and are almost always
surrounded by a simple, thin, mucilaginous sheath. Athough hyaline
at maturity in some species, spores may become brown with age. Asci
are bitunicate, having fissitunicate dehiscence and are provided
with an ocular chamber and faint apical ring. The neck in M.
eburnea is surrounded by a clypeus, comprising compact
brown-walled angular to globose fungal cells. Fungi with
Massarina-like characteristics have been identified from wood
submerged in marine and freshwater environments and on decaying
palm fronds.
This genome was sequenced as part of the 1000 Fungal Genomes
Project.
Genome Reference(s)
Haridas S, Albert R, Binder M, Bloem J, LaButti K, Salamov A, Andreopoulos B, Baker SE, Barry K, Bills G, Bluhm BH, Cannon C, Castanera R, Culley DE, Daum C, Ezra D, González JB, Henrissat B, Kuo A, Liang C, Lipzen A, Lutzoni F, Magnuson J, Mondo SJ, Nolan M, Ohm RA, Pangilinan J, Park HJ, Ramírez L, Alfaro M, Sun H, Tritt A, Yoshinaga Y, Zwiers LH, Turgeon BG, Goodwin SB, Spatafora JW, Crous PW, Grigoriev IV
101 Dothideomycetes genomes: A test case for predicting lifestyles and emergence of pathogens.
Stud Mycol. 2020 Jun;96():141-153. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2020.01.003
