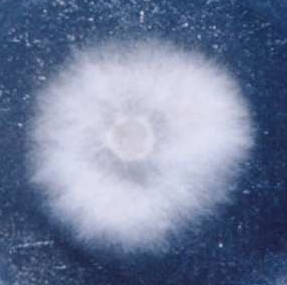
The phytopathogenic fungus Sclerotinia borealis Bubak & Vleugel, which is an ascomycete belonging to the family Sclerotiniaceae of the order Helotiales, has a broad host range and causes diseases in at least 17 plant genera from the families Alliaceae, Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Campanulaceae, Fabaceae, Iridaceae, Pinaceae, and Poaceae (notably wheat and corn). S. borealis is a psychrophilic necrotrophic fungus with an optimum growth temperature between 4°C and 10°C. The main specific feature of the disease called “snow mould” is a white mycelium and sclerotia growth on dead plant tissues. S. borealis is distributed mostly in northern regions (Japan, North America, Scandinavia, and Russia). However, the biology of S. borealis and its phylogenetic relationships to the other species of Sclerotiniaceae are still poorly understood. Sequenced strain S. borealis F-4128 was obtained from All-Russia Collection of Microorganisms (VKM).
The genome sequence and gene models of Sclerotinia borealis F-4128 were not determined by the Joint Genome Institute (JGI), but were downloaded from Ensembl Fungi on April 11, 2020. Please note that this copy of the genome is not maintained by Ensembl and is therefore not automatically updated. The JGI Annotation Pipeline was used to add additional functional annotation to the author's chromosomes and proteins.
Genome Reference(s)
Mardanov AV, Beletsky AV, Kadnikov VV, Ignatov AN, Ravin NV
Draft Genome Sequence of Sclerotinia borealis, a Psychrophilic Plant Pathogenic Fungus.
Genome Announc. 2014 Jan 23;2(1):. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01175-13
